Data Types
There are different types of data used by programmers in java like Numbers, Alphabets, Images etc. Computer does not know the difference between values like number or alphabets.Each type of data will be categorized into different types which are known as Datatypes in java.Thus, Datatype is a classification of data according to its type that an object or a variable can hold. It is a kind of data storage that contains specific type or range of value. Whenever variable is created a storage is assigned to it according to the datatype.
Two main concepts of Datatypes are -
- Type of data.
- Size allocated to it.
It is classified into two main categories i.e Primitives and Referenced.
There are 8 Primitive Type Datatypes and 4 Referenced Datatypes i.e
Primitives Datatypes - These are built-in or predefined by the language and their definition cannot be changed.
- byte
- short
- char
- int
- long
- float
- double
- boolean
Referenced Datatypes - These are user defined datatypes. these are created by user no reserve keywords are used.
- Array
- Class
- Enum
- Interface
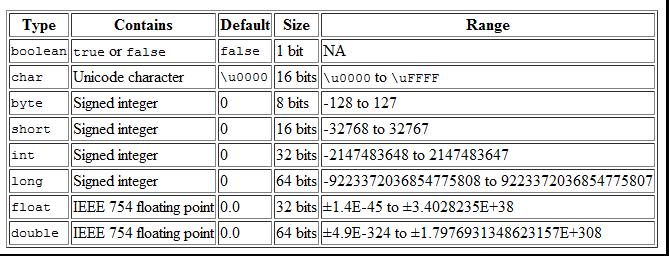
Each Datatypes has its own size and range in memory.
Default Value: They have specific default value, in case user doesn't initialize any value to a variable then default value according to its datatype will be assigned.
Size: Size specify the space that a variable will take to store in memory,this will done according to its datatype.
Range: Range specify the range number in which a value can be initialize to a variable, this can also be done according to datatypes to which it assign. If user initialize a variable out of its range then compiler will generate an error.

Thanks for providing accurate content on Data Types.
ReplyDelete